Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
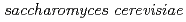
Onuki, Toshihiko; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Ozaki, Takuo; Narumi, Issei; Francis, A. J.*; Iefuji, Haruyuki*; Sakai, Takuro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sato, Takahiro; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.378 - 382, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.38(Instruments & Instrumentation)We examined the accumulation of Cs and Co, and the presence of other elements in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cells by the particle induced X-ray emission (PIXE) system, which has low concentration detection limit of ppm, developed at the TIARA facility, JAERI, and by energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) equipped with scanning electron microscope. Addition of 1mM Cs did not have any effect on the growth of the yeast, whereas 0.5 mM Co inhibited its growth. Cells exposed to Cs showed an increase in Cs peak intensity, decrease in P, and no change in Fe, Zn and K with time. In the presence of Co, the intensity of Co and Fe peaks increased with time up to 21 hours while P, K and Zn exhibited no clear trend. These results suggest that PIXE is a useful technique to detect low concentration of elements in microbial cells as well as monitor their changes as function of growth.
Ozaki, Takuo; Ambe, Shizuko*; Abe, Tomoko*; Francis, A. J.
Biological Trace Element Research, 90(1-3), p.273 - 281, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:6.56(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
Amano, Hikaru
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 73(12), p.1351 - 1352, 1997/12
no abstracts in English
Amano, Hikaru; Atarashi, Mariko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 39(11), p.929 - 931, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Amano, Hikaru
JAERI-Research 96-029, 190 Pages, 1996/06
no abstracts in English
Amano, Hikaru; Atarashi, Mariko
Int. Workshop Proc., Improvement of Environmental Transfer Models and Parameters, 0, p.136 - 145, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Amano, Hikaru
Fusion Technology, 28, p.797 - 802, 1995/10
no abstracts in English
Onuki, Toshihiko; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Accumulation of Cs by unicellular fungus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the presence of minerals have been studied to elucidate the role of microorganisms in the migration of radioactive Cs in the environment. With carbon source, higher amounts of Cs was accumulated in the cells than in the resting condition without carbon source. In the presence of mineral in the agar medium, the radioactivity in the yeast cells with different minerals were in the order of the inverse of Kd of minerals. These results strongly suggest that the yeast accumulates radioactive Cs competitively with minerals.